#history #ancient #near_east #essay
How Geology Shaped Ancient Near Eastern Civilization
The Fertile Crescent is a region in the Near East that stretches from the Mediterranean Sea to the Zagros Mountains in the east, down to the Persian Gulf in the south. It is much more conducive to agriculture when compared to its surroundings due to both geographic variety and abundance of water.
Tectonic Plates
Before I dive into the geography, I think it's really interesting to take a brief look at the underlying structure. The Near East lies on an intersection of the Arabian Plate, the African plate and the Eurasian Plate.
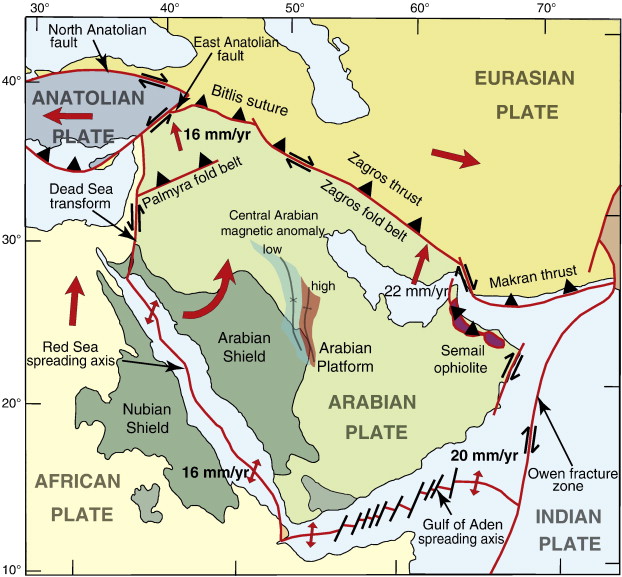
To touch briefly on each side, in the south the African and Arabian plates are diverging (moving away from each other) giving us the Red Sea. In the east the plates are transforming (rubbing against each other) giving us the Dead Sea Transform or the Dead Sea Rift.
More relevant to this discussion, in the north, the Arabian Plate and the Eurasian plate are converging (moving towards each other at about 3cm per year) to form the Zagros Fold and Thrust Belt. The plates are coming together with the Arabian plate being forced below the Eurasian plate. The Arabian plate's being pushed down forms a gradual depression from the Arabian sea to the Mediterranean Sea where the Euphrates and Tigris rivers lie. The Eurasian Plate's being pushed up forms the Zagros Mountains!


Now that we see the basic structure of the Near East and the kind of shapes and movements these plates are causing, let's see what the topographical and ecological effects are.
Arabian Desert
In the middle of the Arabian continent we have the Arabian Desert, a huge, barren region of endless dunes.


In antiquity this acted as a physical barrier. Crossing it directly was impossible during the 3rd century BC and human travel was restricted to the Euphrates and the Tigris.
Farming and settlement was possible along the rivers during the winter and spring months, but come summer and autumn it became increasingly difficult.
Zagros Steppe
While the mountains themselves were a challenge, the steppe surrounding them was very temperate. Annually the region receives between 400mm and 800mm of rain annually which is just enough to support dry farming, a method of farming that relies on rainfall.
The map below depicts the 200mm and 400mm isohyets. Notice the 400mm line circling the Zagros Mountains reaching all the way down to southern Levant region in the East. At 400mm dry farming is almost guaranteed to be successful!
![[Screen Shot 2021-07-08 at 9.30.42 PM.png]]
The Rivers
Water Sources
Wet Farming is agriculture that relies on irrigation or other direct watering methods.
Dry Farming is agriculture that relies on rain.
An Isohyet is an area drawn on a map that receives a specific amount of rainfall.
Dry farming requires at least 200mm of rain fall annually, thus is restricted to the 200mm isohyet and above. This area surrounds the Zagros Mountains and stretches east towards the Mediteranean Sea and provides enough rainfall for crops to flourish naturally. This area can be considered the mediteranean steppe.
From the Zagros Mountains south to the Persian Gulf there is little to no rain fall, but there exists two large rivers that provide more than enough water for crops. These are the Euphrates in the west and the Tigris in the east.
These two water sources enable two different types of farming.
These two sources of water make the region incredibly fertile compared to the surrounding area.
To the south west of the fertile crescent (the region the crescent is surrounding) we have the Arabian Desert. This stretch of barren land was effectively impenetrable in ancient times and was avoided at all costs.
Biodiversity
The near east is known for it's biodiversity which was the catalyst for specialization, trading, and agriculture as we know it today.
Why was there so much diversity? What are some examples of the diversity?
Civilization
The Fertile Crescent provided the resources necessary for civilization to sprout. Cities such as Uruk in southern Babylonia, Ur in middle Mesopotamia and Nineveh in southern Turkey are some great examples of civilizations that flourished in this region.
What exactly from the environment helped them flourish?
